|
23.01.2012
Distributed Research Infrastructure for HydroMeteorology The proposed DRIHM (Distributed Research Infrastructure for Hydro-Meteorology) project intends to develop a prototype e-Science environment to facilitate this collaboration and provide end-to-end HMR services (models, datasets and post-processing tools) at the European level, with the ability to expand to global scale. The objectives of DRIHM are to lead the definition of a common long-term strategy, to foster the development of new HMR models and observational archives for the study of severe hydrometeorological events, to promote the execution and |
|
22.01.2012
A worldwide e-Infrastructure for NMR and structural biology The main objective of WeNMR is to establish an e-Infrastructure-based global virtual research community for structural biology in the life sciences. To this end six objectives are defined: |
|
22.01.2012
|
|
22.01.2012
|
|
22.01.2012
In the past few years the lagoon (technically a haff-delta) has been threatened by a decrease in water quality due to industrial, urban and agricultural effluents, but thanks to the Ria’s economic, ecologic and cultural importance, there is a strong push to preserve its ecosystem. The key to long-term sustainability is efficient management and to achieve that, decision-makers need to have a solid understanding of this environment. |
|
22.01.2012
|
|
22.01.2012
|
|
22.01.2012
|
|
22.01.2012
Pulling information out of a genome has proved to be a challenging task, which requires complex statistical tools and powerful computers to run the analysis. And if results are to be delivered in a reasonable timeframe, you’d better ask for fast computers as well. This sort of computing power is not available to all researchers interested in how animals inherit their physical traits. To counter this problem, Dr Sara Knott from the University of Edinburgh and her team developed GridQTL, a grid-based platform that provides fast and robust analysis to identify trait-related genome regions. These are called quantitative trait loci (QTL). Knott explains: “QTL are regions of the genome that have an effect on a given physical trait.” A knowledge of the QTL involved in the expression of a trait is crucial for our understanding of variation between individuals and how traits are passed on from generation to generation, she adds. |
|
22.01.2012
Identifying as many viruses as possible improves the chances of correct diagnostics and helps to determine the best treatment for patients. Knowing which virus is responsible for which disease is also very important to detect potential epidemics or to assess the seriousness of viral infections. |
|
 Англійська Англійська
 Українська Українська
|
 Увійти Увійти
 Реєстрація Реєстрація
|

|
Випуск 4
| © 2011-2012, Інститут теоретичної фізики ім.М.М. Боголюбова | Інформація про сайт | Розроблено в MCG |

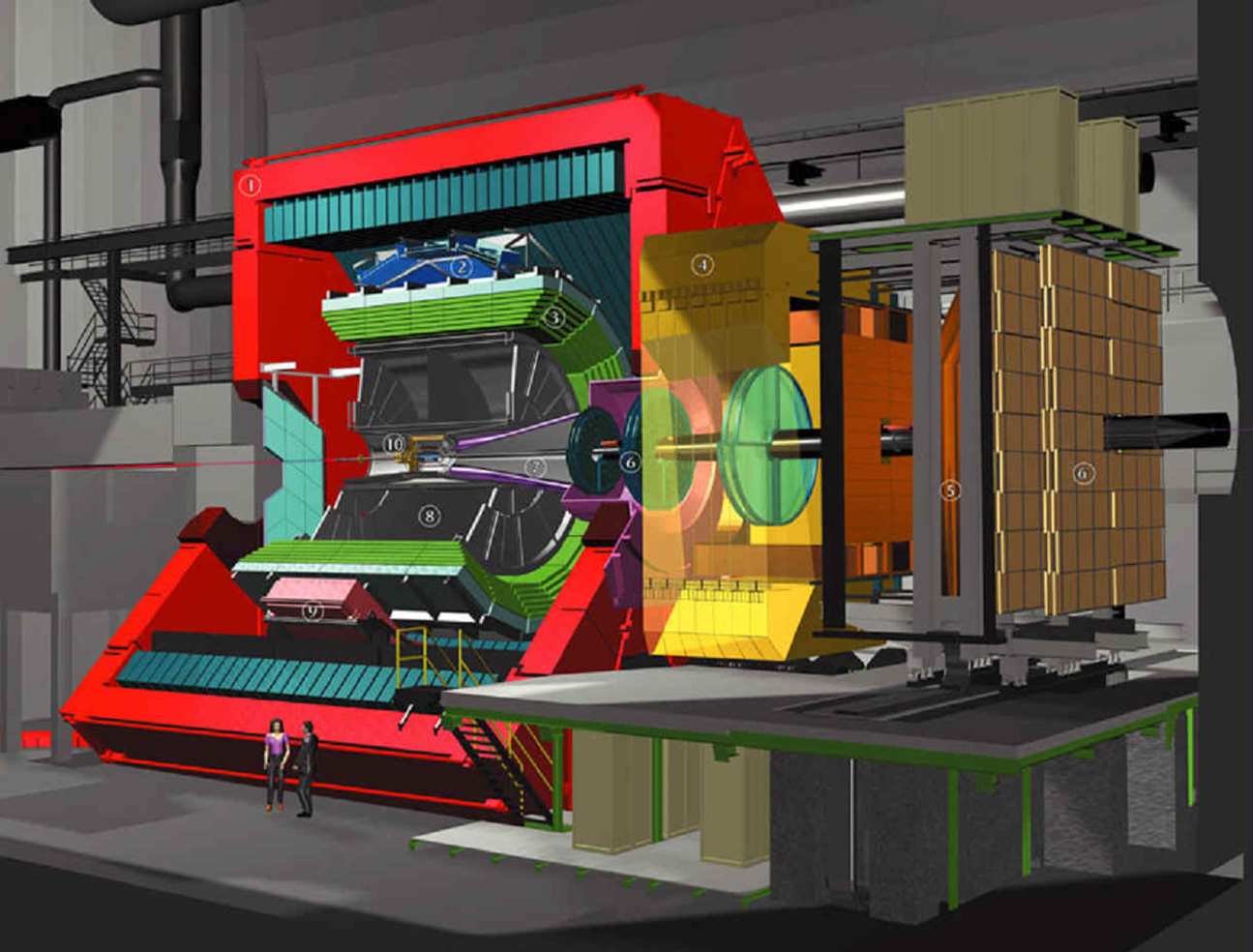 The
The  Grid computing is helping palaeontologists to understand better how dinosaurs moved around and what roles they played in their ancient world.
Grid computing is helping palaeontologists to understand better how dinosaurs moved around and what roles they played in their ancient world. The Aveiro Lagoon in Portugal is a national treasure. With a length of about 45km and separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a sandy dune barrier, this shallow lagoon is one of Europe’s last pristine coastal marshes and a haven for many bird species.
The Aveiro Lagoon in Portugal is a national treasure. With a length of about 45km and separated from the Atlantic Ocean by a sandy dune barrier, this shallow lagoon is one of Europe’s last pristine coastal marshes and a haven for many bird species.  Velibor Isailovic at the Jaroslav Cerni Institute of Water Resources in Belgrade, Serbia is leading the development of LizzaPAKP, an application designed to simulate groundwater flow using a finite element numerical model. The application integrates PAKP (a numerical solver which uses Darcy’s Law of flow to describe how water moves through porous materials) with Lizza a user-friendly desktop interface.
Velibor Isailovic at the Jaroslav Cerni Institute of Water Resources in Belgrade, Serbia is leading the development of LizzaPAKP, an application designed to simulate groundwater flow using a finite element numerical model. The application integrates PAKP (a numerical solver which uses Darcy’s Law of flow to describe how water moves through porous materials) with Lizza a user-friendly desktop interface. Developing a Global Imaging Laboratory based on Grid/Cloud computing to help develop drugs for Alzheimer's disease
Developing a Global Imaging Laboratory based on Grid/Cloud computing to help develop drugs for Alzheimer's disease DNA sequencing is becoming faster and cheaper, outrunning the ability to store, transmit and analyze the data.
DNA sequencing is becoming faster and cheaper, outrunning the ability to store, transmit and analyze the data. Respiratory infections are the main reason why children under five end up in hospital. However, in up to 40% of the cases it’s not possible to define the exact cause of the disease and this means that there are viruses still unknown to science.
Respiratory infections are the main reason why children under five end up in hospital. However, in up to 40% of the cases it’s not possible to define the exact cause of the disease and this means that there are viruses still unknown to science.